DualRefine
DualRefine: Self-Supervised Depth and Pose Estimation Through Iterative Epipolar Sampling and Refinement Toward Equilibrium
Abstract
Self-supervised multi-frame depth estimation achieves high accuracy by computing matching costs of pixel correspondences between adjacent frames, injecting geometric information into the network. These pixel-correspondence candidates are computed based on the relative pose estimates between the frames. Accurate pose predictions are essential for precise matching cost computation as they influence the epipolar geometry. Furthermore, improved depth estimates can, in turn, be used to align pose estimates.
Inspired by traditional structure-from-motion (SfM) principles, we propose the DualRefine model, which tightly couples depth and pose estimation through a feedback loop. Our novel update pipeline uses a deep equilibrium model framework to iteratively refine depth estimates and a hidden state of feature maps by computing local matching costs based on epipolar geometry. Importantly, we used the refined depth estimates and feature maps to compute pose updates at each step. This update in the pose estimates slowly alters the epipolar geometry during the refinement process. Experimental results on the KITTI dataset demonstrate competitive depth prediction and odometry prediction performance surpassing published self-supervised baselines.
Contributions
- We introduce an iterative update module that is based on epipolar geometry and direct alignment.
- These updates refine theinitial estimates made by the single-frame model.
- The model is designed within a deep equilibrium framework, which allows the model to converge to a fixed point.
Overall architecture
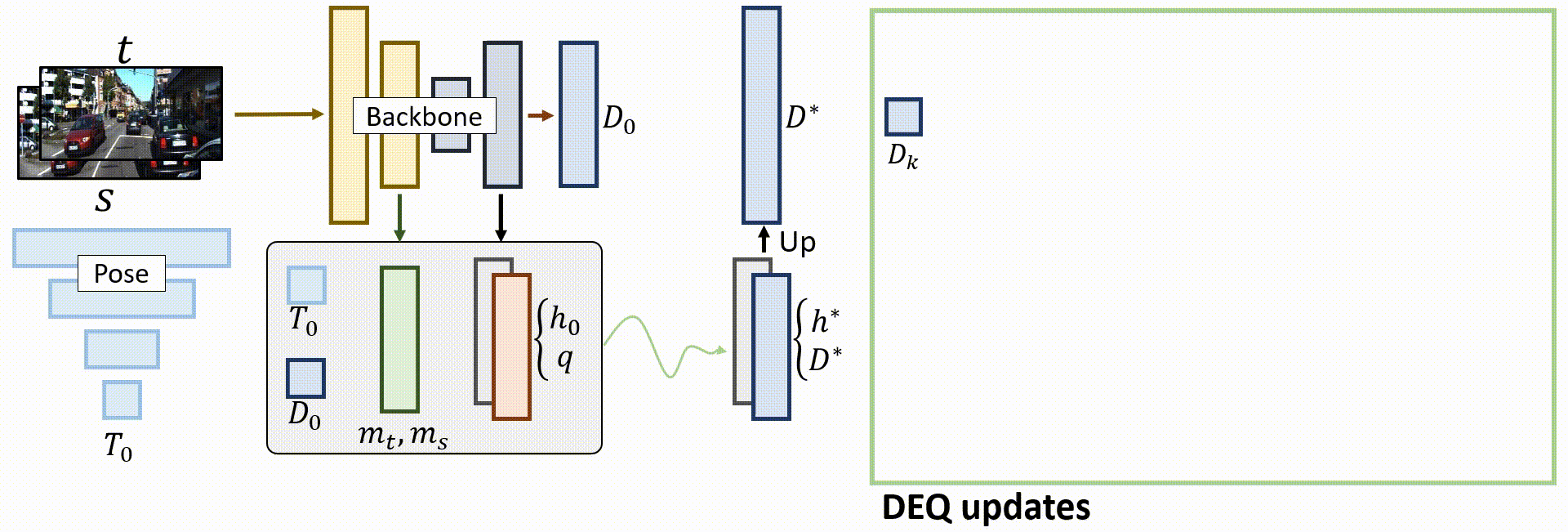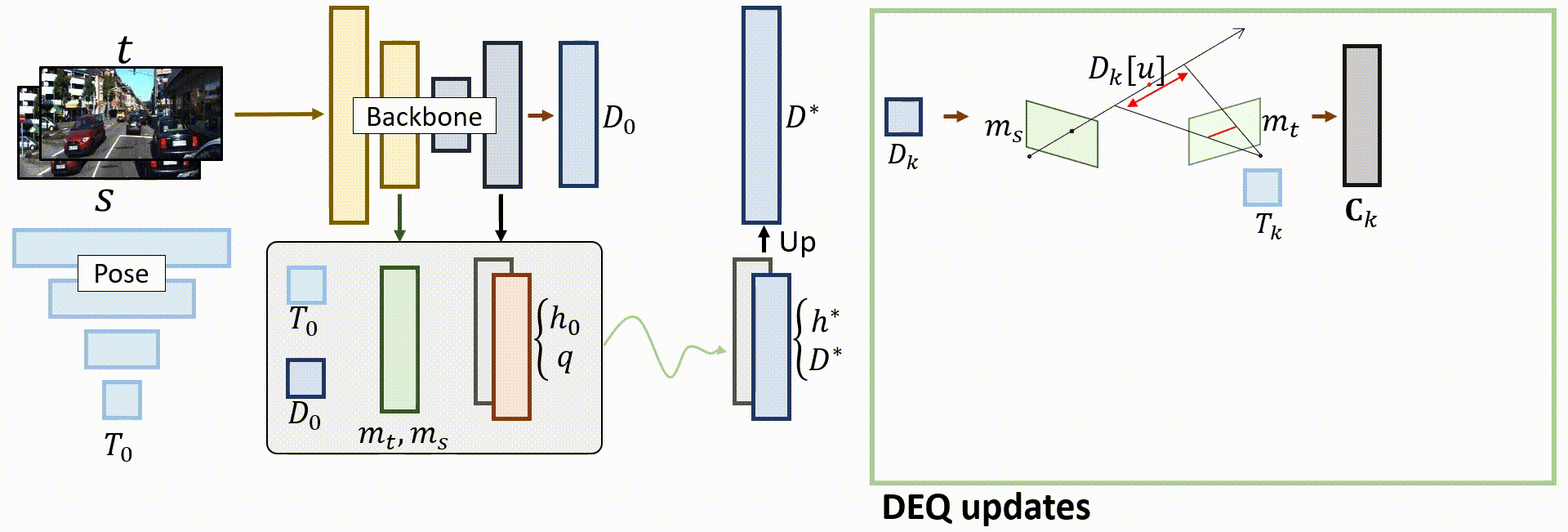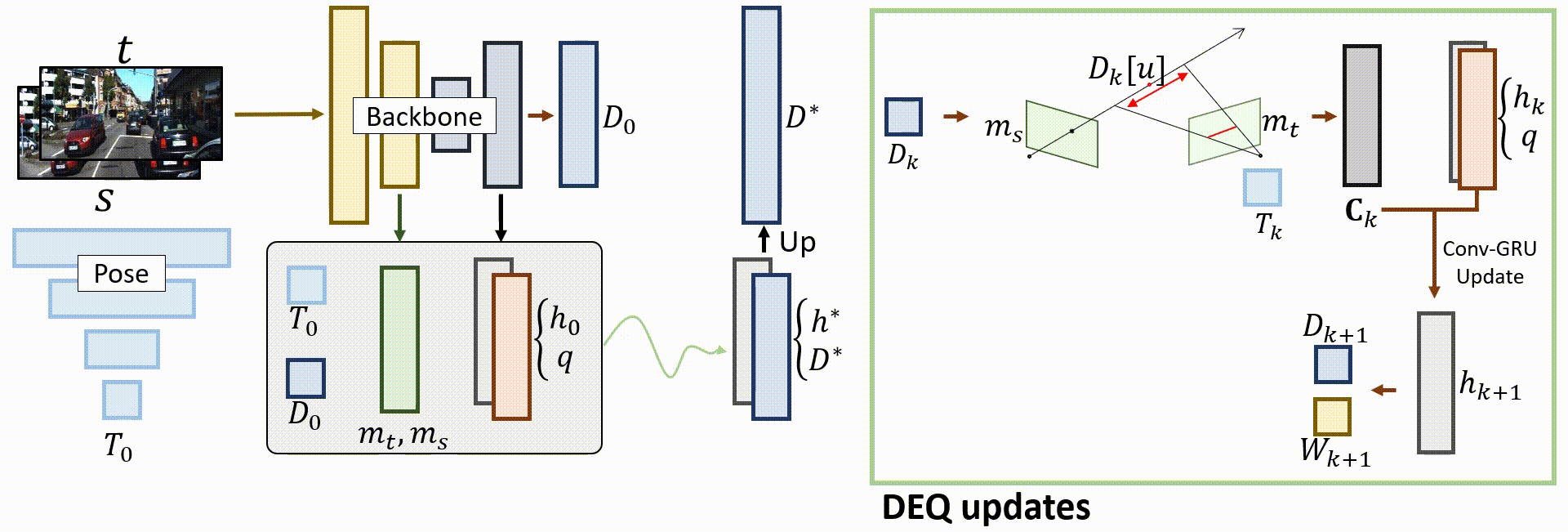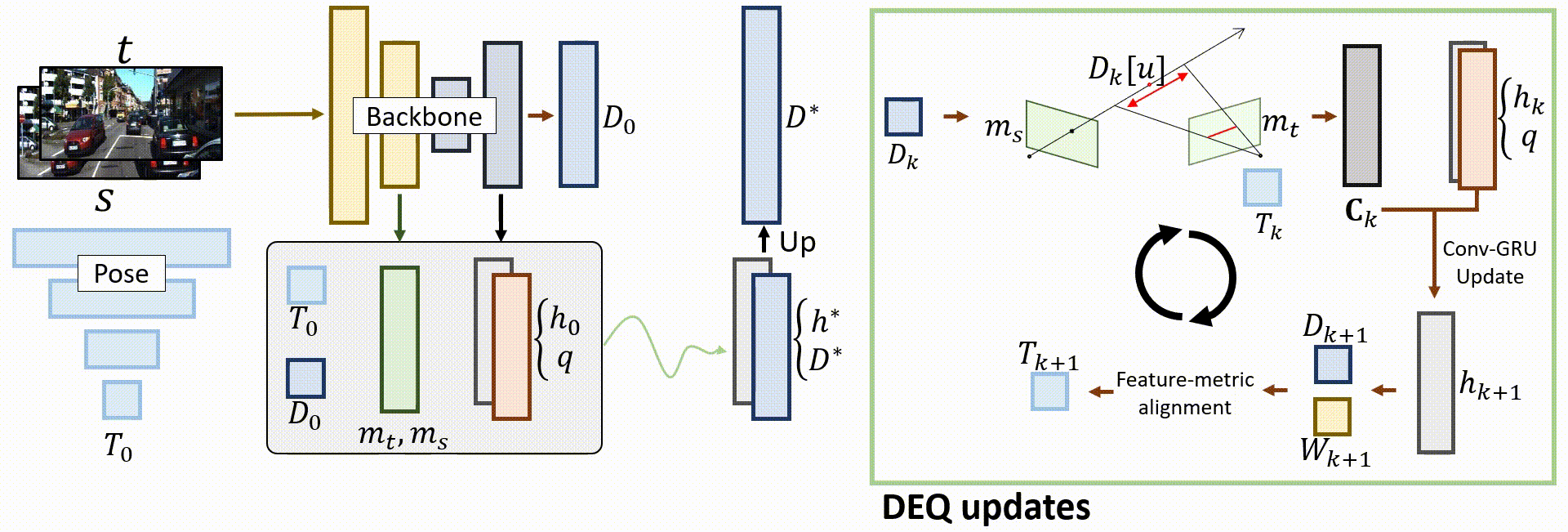
Given a pair of source and target images, the teacher model predicts an initial depth D0 and pose T0, as well as initial hidden states that will be updated. DEQ-based alignments are then performed to find the fixed point and output the final predictions.
Experiments
Comparison with state-of-the-art methods
A comparative evaluation of the DualRefine model with recent leading self-supervised multi-frame depth estimation methods using the KITTI Eigen test split dataset. The significant improvement in the $$\delta_1$$ metric indicates that the DualRefine model is able to produce more accurate depth estimates for the inlier pixels.
Significance of pose refinement
The model trained without pose refinement exhibit the poorest performance. In contrast, models employing pose refinement with learned per-pixel weights and refined pose for computing consistency masks achieve the best results overall. This highlights the crucial role of pose refinement in enhancing the accuracy of depth estimation.
Depth per iteration
The depth error per iteration for the DualRefine model. The model converges to a fixed point after 6 iterations.
On the left shows the initial depth estimates and on the right is the refined depth at each iteration. The refinement visibly helps to improve the depth estimates around thin structures, but may be more susceptible to dynamic objects and non-lambertian surfaces. Note that the speed is slowed down for visualization purposes. Actual speed on our device with an RTX 3090 is around 15 fps.